Psoriasis and diabetes are different illnesses that may seem disconnected at first glance. However, recent studies have shed light on a fascinating connection between these conditions that has captivated the attention of medical experts and those affected by them. In this article, we'll dive into the complex relationship between psoriasis and diabetes, uncovering the causes, symptoms, and management techniques for individuals facing both challenges.
Psoriasis, an ongoing autoimmune skin disorder, impacts millions globally. Similarly, diabetes is a widespread health issue involving irregular blood sugar levels. It's crucial to recognize how these two problems overlap so that patients can receive well-rounded care. When healthcare providers understand the shared risk factors, mechanisms, and implications of psoriasis and diabetes, they can develop more effective strategies for managing both conditions.
In the following sections, we'll deeply dive into the intricacies of psoriasis and diabetes. We'll untangle their connections while discussing common symptoms and offering guidance on managing these conditions simultaneously. Our goal is to equip patients and healthcare professionals with valuable knowledge that can lead to better outcomes and an improved quality of life for those struggling with psoriasis and diabetes.
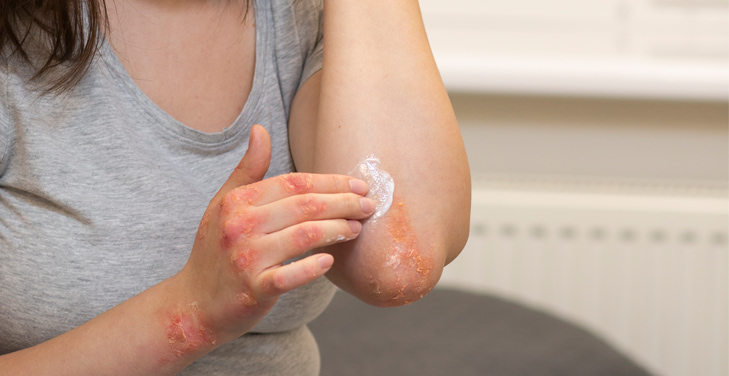
Psoriasis and diabetes often coexist, and understanding their connection is crucial for comprehensive care.
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis, an irritating and intricate autoimmune skin disease, profoundly impacts countless individuals worldwide. It is characterized by an overgrowth of skin cells, leading to the notorious raised, reddened plaques adorned with silvery scales. Understanding the nature of this condition is vital for both patients and healthcare professionals.
Definition and Explanation of Psoriasis
Let's break it down: psoriasis is rooted in a faulty immune system that mistakenly targets healthy skin cells, resulting in their speedy reproduction. This immune snafu triggers a cascade of inflammation, causing the skin to swell, thicken and flake. While experts haven't pinpointed the exact cause, genetics and environmental factors are believed to play prominent roles.
Prevalence and Demographics
Psoriasis knows no bounds; it can strike people from all walks of life regardless of age or ethnicity. Roughly 2-3% of the world's population is caught in its clutches. And don't be fooled by stereotypes - psoriasis doesn't discriminate between males and females or among children, teenagers, and adults. The age at which symptoms arise varies greatly - some experience it as kids, while others must endure it later in life.
Common Symptoms and Types of Psoriasis
This sneaky disease takes on different forms - each with its unique characteristics. Plaque psoriasis is the most common type, showing off its signature patches on elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. But there are other players in this game - guttate, pustular, inverse, and erythrodermic psoriasis -each distinguished by distinct manifestations on various body parts. Symptoms are universal - itching, pain, and discomfort are frequent culprits that can significantly disrupt a patient's day-to-day existence.
The Connection Between Psoriasis and Diabetes
Psoriasis and diabetes share a complex relationship, with chronic inflammation as a common thread. Understanding this connection is crucial for managing conditions effectively and improving patient outcomes.
Recent research has revealed a strong connection between these seemingly unrelated conditions, shedding light on shared underlying processes and risk factors. This discovery is crucial for healthcare professionals seeking comprehensive care for patients with psoriasis and diabetes.
Research and Studies Establishing the Link
Latest studies have uncovered the intricate relationship between psoriasis and diabetes. Scientists have noticed a higher prevalence of diabetes among those with psoriasis and vice versa. This two-way relationship has sparked interest in uncovering the underlying mechanisms, leading to findings that suggest chronic inflammation is a significant factor in both conditions. Inflammatory processes appear to be a key point of convergence in connecting psoriasis and diabetes.
Shared Risk Factors and Genetic Predisposition
Apart from inflammation, both psoriasis and diabetes share common risk factors. Obesity is a well-known risk factor for both diseases, further solidifying their link. Moreover, growing evidence supports the presence of genetic predisposition factors that make individuals susceptible to developing psoriasis and diabetes. Further understanding this genetic aspect could give us valuable insight into how these conditions develop.
The Role of Inflammation in Both Conditions
Inflammation seems to be a vital player in both conditions as it plays a central role in chronic skin inflammation in psoriasis, whereas systemic inflammation occurs with diabetes. Consequently, this inflammatory environment can lead to insulin resistance, an essential factor contributing to type 2 diabetes development. Expanding our knowledge about these shared inflammatory pathways holds immense potential for discovering novel treatments that target this underlying process in both diseases.
Psoriasis and Diabetes: Shared Symptoms
The connection between psoriasis and diabetes goes beyond their basic inner workings – it also shows up in similar symptoms. Recognizing these overlapping signs is critical for diagnosing and caring for patients, as those with both conditions may face compounded health issues.
Discussing the Overlapping Symptoms
Let's dive into some of the main shared symptoms between psoriasis and diabetes. One major one is chronic inflammation. For psoriasis, this takes the form of red, swollen, and scaly skin. In diabetes, systemic inflammation contributes to insulin resistance and impaired glucose processing. Both illnesses are also linked to a higher risk of heart problems, highlighting the importance of identifying and managing these common indicators.
How Skin Inflammation Can Affect Diabetes Management
It's worth noting how skin inflammation can affect individuals with psoriasis and diabetes. Inflamed skin may be more vulnerable to infections, disrupting efforts to control blood sugar levels for those with diabetes. Additionally, the ongoing stress of managing visible psoriasis symptoms can worsen blood sugar management in these patients.
Impact of Diabetes on Psoriasis Severity
On the flip side, diabetes can have an impact on the severity of psoriasis symptoms as well. When diabetes isn't well managed, it can aggravate skin inflammation and worsen psoriasis. High blood sugar levels could also weaken the body's immune response, leading to more difficulty controlling flare-ups caused by psoriasis. Thus, a crucial part of managing both conditions effectively is controlling blood glucose levels.
Understanding these connections between shared symptoms is crucial for healthcare providers looking to provide comprehensive care for individuals facing both psoriasis and diabetes simultaneously.
Managing Psoriasis and Diabetes Together
When managing both psoriasis and diabetes simultaneously, some unique challenges and considerations must be considered. This requires a comprehensive approach that addresses each condition's specific needs while recognizing how they may affect one another. This section will delve into some strategies for effectively managing these two conditions together.
Lifestyle Modifications and Their Importance
One of the critical elements in successfully managing both psoriasis and diabetes is making necessary lifestyle changes. Encouraging patients to adopt healthy habits, such as eating a well-balanced diet, staying physically active, and practicing stress management, can profoundly impact both conditions. Weight management is especially crucial as it is a shared risk factor for psoriasis and diabetes. As healthcare professionals, it is essential to provide guidance and support for patients working towards these positive lifestyle modifications.
Medications and Treatment Options
In addition to lifestyle changes, medication plays a vital role in managing psoriasis and diabetes. Dermatologists may prescribe topical treatments or systemic medications to control psoriasis symptoms, while endocrinologists may recommend oral medications, insulin therapy, or other injectable options for diabetes management. Healthcare providers must coordinate care between these two specialties and consider possible interactions when treating patients with both conditions.
Collaborative Care Between Dermatologists and Endocrinologists
Collaboration between dermatologists and endocrinologists is critical in providing the best care for individuals with comorbid psoriasis and diabetes. By working together, treatment plans can align seamlessly and complement each other to optimize overall management strategies. Regular communication between specialists allows for any necessary adjustments, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes.
Tips for Preventing Diabetes Complications in Psoriasis Patients
Effectively managing diabetes and comorbid psoriasis requires constant attention to prevent potential complications. The presence of psoriasis can exacerbate diabetes-related issues, making it crucial for individuals to take proactive measures to maintain their overall health and well-being.
Blood Sugar Monitoring and Control
Maintaining a stable blood sugar level is vital for those with both conditions. This involves closely monitoring blood sugar levels according to the prescribed schedule and promptly reporting any irregularities to healthcare providers. Achieving and sustaining target blood sugar levels can significantly reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Diet and Nutrition Recommendations
Diet plays a significant role in managing both psoriasis and diabetes. Encouraging patients to follow a diet that prioritizes whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables while limiting refined sugars and saturated fats is essential. Since specific dietary triggers for psoriasis vary from person to person, recommending an elimination diet may help identify any potential exacerbators.
Exercise and Stress Management
Physical activity helps control blood sugar levels and has stress-relieving benefits that can benefit individuals with both conditions. Creating a personalized exercise plan based on the patient's abilities and preferences is recommended. Additionally, incorporating stress management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or relaxation exercises can help alleviate stress, which is known to trigger psoriatic flare-ups.
Medication Adherence
Ensuring medication adherence for both psoriasis and diabetes medications is crucial for preventing uncontrolled symptoms and possible complications. Regular medication reviews and open communication with healthcare providers can address any concerns or side effects affecting adherence.
Through offering practical tips and guidance like these, healthcare professionals can empower individuals with comorbid psoriasis and diabetes to proactively manage their conditions while reducing the risk of complications.
The Bottom Line
In the complex dance between psoriasis and diabetes, we have unveiled a dynamic relationship beyond their superficial dissimilarities. This article has shed light on the shared processes, symptoms, and hurdles encountered by people with both illnesses. Grasping the convergence of psoriasis and diabetes is crucial for medical professionals and patients.
Comprehending the link between these conditions is not an exercise in theory; it holds pragmatic implications for clinical care. Patients grappling with comorbid psoriasis and diabetes necessitate comprehensive management that considers the unique demands of each ailment while navigating their intricate interdependence. The collaboration of dermatologists and endocrinologists is pivotal in ensuring treatment strategies complement one another, enhancing outcomes and ultimately improving the overall quality of life for those affected.
As we reach the culmination of this exploration, we must emphasize the significance of early detection, proactive treatment, and ongoing support for individuals living with psoriasis and diabetes. Through knowledge, awareness, and a united approach to healthcare, we can strive towards bettering the well-being and health outcomes of those facing the dual challenge posed by these intimately connected conditions.
Also Read:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Psoriasis and Diabetes
-
What is diabetes psoriasis?
There is no medical term "diabetes psoriasis." However, these are separate conditions, with diabetes affecting blood sugar control and psoriasis involving skin inflammation.
-
How to treat psoriasis in diabetes?
Treating psoriasis in individuals with diabetes may require a multidisciplinary approach involving dermatologists and endocrinologists and may include medications, lifestyle modifications, and careful blood sugar management.
-
What is the link between psoriasis and diabetes?
The link between psoriasis and diabetes involves shared risk factors, inflammation, and a higher prevalence of one condition in individuals with the other. Both conditions may exacerbate each other's symptoms.
-
How do you tell diabetes rash from psoriasis?
Distinguishing between a diabetes-related skin issue and psoriasis may require a medical evaluation. A healthcare professional can examine the rash's characteristics, location, and associated symptoms to provide an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.

