In the always evolving world of medicine, new discoveries often challenge our beliefs about established treatments. One such discovery has cast a shadow of doubt over Lisinopril, a trusted medication for heart health. Recent findings suggest a possible connection between Lisinopril and diabetes, sparking discussions among doctors and medical professionals.
This revelation has put both healthcare providers and patients at a crossroads, balancing the need for cardiovascular treatment with concerns for metabolic health. The unfolding situation has led to closer scrutiny of how Lisinopril may affect blood sugar levels, leading to a united effort to gain a better understanding of the issue.
These discussions have initiated an exploration into the complexities of how medications can impact our bodies, prompting us to rethink what we thought we knew in light of this newfound knowledge.
Lisinopril and diabetes are subjects of increasing interest; understanding their relationship is crucial for comprehensive healthcare.
What is Lisinopril?
Lisinopril, a commonly prescribed medicine, falls into the class of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, known for effectively treating various heart conditions. It works by preventing the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, leading to widened blood vessels and improved heart function. Given its effectiveness in managing high blood pressure, heart failure, and other cardiovascular issues, Lisinopril is a go-to treatment in this field.
Definition and Function of Lisinopril
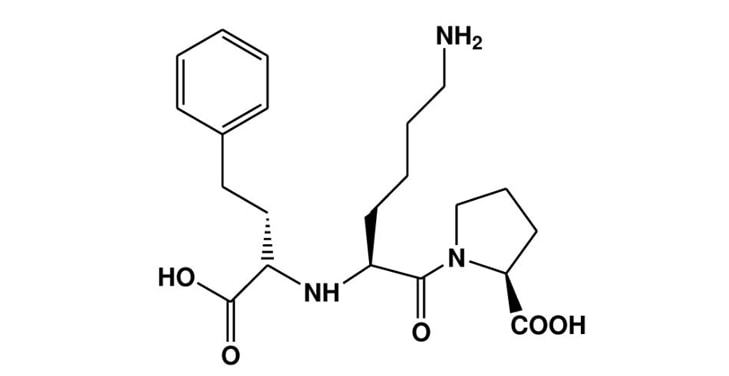
In scientific terms, Lisinopril is referred to as (S)-1-[N2-(1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-L-lysyl]-L-proline dihydrate. Its key role lies in regulating the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system which controls blood pressure levels. By inhibiting ACE activity, it reduces the production of angiotensin II - a substance that constricts blood vessels - resulting in relaxed arteries and lower resistance to blood flow.
Common Medical Uses and Conditions Treated
Doctors often prescribe Lisinopril for hypertension as it poses significant risks to heart health. In addition to managing this condition, it has proven beneficial for treating heart failure, diabetic nephropathy (kidney disease caused by diabetes), and post-heart attack care. The medication can be used alone or combined with other drugs like diuretics or calcium channel blockers for better outcomes.
Mechanism of Action in the Body
Upon ingestion, Lisinopril is rapidly absorbed by the body and converted into its active form called Lisinoprilat. This metabolite targets the kidneys where it hinders bradykinin's breakdown - a substance that promotes vasodilation (widening of blood vessels). This leads to lower blood pressure levels and may even offer extra protection for the heart. Its long-lasting effects allow once-daily dosing, making it convenient for patients.
Lisinopril's diverse mechanisms make it a powerhouse in treating cardiovascular issues, cementing its role as a top choice for hypertension and related conditions.
The Lisinopril and Diabetes Debate
Amidst its widespread use in cardiac care, a discussion has emerged regarding Lisinopril's potential association with diabetes mellitus. Research studies have shed light on this complex topic, presenting varying results and stimulating further investigation into the relationship between these two medical phenomena.
Research Studies Exploring the Potential Link
Scientists have conducted several studies aiming to understand whether taking ACE inhibitors like Lisinopril could impact glucose (sugar) metabolism, increasing one's chances of developing diabetes. While some investigations indicate a possible link between these medications and higher diabetes risk, others have found no significant correlation.
Conflicting Findings in Existing Literature
The existing literature showcases conflicting findings on this topic - some studies suggesting an elevated risk of diabetes with Lisinopril use while others disputing such claims. These differences could be attributed to variations in research methods, patient populations studied, and duration of exposure to Lisinopril, highlighting the need for careful analysis before drawing any conclusions.
Expert Opinions and Perspectives on the Matter
Given the lack of consensus among research findings, expert opinions play a crucial role in guiding clinical practice. Some healthcare professionals advise close monitoring of patients at risk for diabetes when prescribing Lisinipril; others stress evaluating each individual's risks versus benefits before deciding on treatment options. This ongoing discourse highlights the complexity of establishing causation versus association between Lisinopril and diabetes and emphasizes adopting a comprehensive approach when addressing this matter.
It is crucial for medical providers to stay updated on emerging research, use discretion when prescribing Lisinopril, and engage in open and informative discussions with their patients about potential risks and benefits associated with this medication, particularly in regards to its supposed relationship with diabetes.
People Also Read:
Lisinopril's Impact on Blood Glucose Levels
The effect of Lisinopril, an ACE inhibitor, on blood sugar levels has generated considerable interest in the medical world. It's crucial for healthcare providers prescribing this medication and individuals managing chronic conditions to understand its subtle relationship with glycemic control.
Examination of Studies Investigating Lisinopril's Effect on Blood Sugar
Studies on Lisinopril's influence on blood glucose levels have produced mixed results. While some suggest a link between ACE inhibitors like Lisinopril and changes in glucose metabolism, others have not consistently demonstrated a significant effect on blood sugar levels.
Insights Into Potential Mechanisms That May Contribute to Changes in Glucose Levels
The exact mechanisms by which Lisinopril affects blood sugar are not fully understood. Some theories propose that it may impact insulin sensitivity or secretion, adding complexity to understanding its impact on glycemic control. The intricate interplay between the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and glucose regulation also plays a role.
Consideration of Dosage and Duration of Lisinopril Use
The dosage and duration of Lisinopril use may contribute to its potential effects on blood sugar levels. Higher doses have been associated with a higher likelihood of glucose-related effects, but more research is needed to determine if these effects are reversible upon discontinuation.
When prescribing Lisinopril, healthcare providers must consider individual patient characteristics such as existing diabetes status and risk factors. Monitoring blood glucose levels is necessary, especially for those at risk for diabetes, in order to provide comprehensive care.
Risk Factors and Precautions
Knowing the risk factors of taking Lisinopril is essential for responsible prescription of this commonly used ACE inhibitor. As healthcare providers navigate the complexities of treating hypertension, they must be mindful of potential risks and implement precautionary measures.
Identification of Individuals at Higher Risk for Diabetes While Taking Lisinopril
One crucial consideration is identifying patients at higher risk for developing diabetes while taking Lisinopril. Patients with pre-existing conditions like obesity, impaired glucose tolerance, or a family history of diabetes may require closer monitoring. Age and ethnicity can also be factors in assessing risk.
Precautionary Measures and Lifestyle Modifications
Implementing precautionary measures and encouraging lifestyle modifications are vital for mitigating potential risks associated with Lisinopril. Health professionals should stress the importance of regular exercise, a balanced diet, and weight management for optimal metabolic health. Educating patients on recognizing early symptoms of diabetes and the importance of regular check-ups empowers them to take charge of their health.
Importance of Regular Monitoring and Communication with Healthcare Professionals
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial for those on Lisinopril, especially at-risk individuals. Open communication between healthcare providers and patients is key in detecting issues early and making necessary adjustments to treatment plans.
Finding the right balance between the cardiovascular benefits of Lisinopril and maintaining metabolic health is critical when prescribing this ACE inhibitor. Identifying risk factors, implementing precautions, and maintaining open communication contribute to personalized care that puts patients first.
Alternative Medications and Treatment Options
Managing high blood pressure can be a tough job for healthcare providers. That's why they have to consider other options when Lisinopril may not be the best choice. Understanding these alternatives is key to finding the right treatment that tackles both heart health and metabolic issues.
Overview of Alternative Medications for Hypertension
There are other medications that can step in if there are concerns about Lisinopril's effect on blood sugar levels. These include Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) like losartan and valsartan, which work differently by blocking the impact of angiotensin II without stopping its production. Calcium channel blockers, such as amlodipine or diltiazem, are also an option as they reduce calcium flow into smooth muscle cells, helping to control blood pressure.
Considerations for Switching Medications
Making the switch from Lisinopril requires a thorough evaluation of individual patient characteristics like pre-existing conditions, tolerance level, and possible side effects. Patient preferences and lifestyle choices also play a vital role in picking the most suitable alternative. For example, someone who experiences coughing as a reaction to ACE inhibitors (including Lisinopril) may get relief from ARBs.
Collaborative Decision-Making with Healthcare Providers
When it comes to switching medications, teamwork makes all the difference. Collaborating with your healthcare provider is critical in finding an alternative medication that aligns with both cardiac goals and potential metabolic concerns. Honest communication empowers patients to actively contribute to their treatment plan, while knowledgeable healthcare professionals factor in medical history and personal preferences.
There's no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to managing high blood pressure. With a variety of medications available, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans according to individual needs while addressing specific worries related to Lisinopril. It's all about teamwork and finding the right balance for each patient.
The Bottom Line
The constantly changing field of heart medication has led to many questions about the connection between Lisinopril and diabetes. Multiple studies have looked into how Lisinopril affects blood sugar levels, but the results are not straightforward. As healthcare providers, we must carefully consider all available research and take into account individual patient factors, like their health history and treatment goals.
Deciding whether to prescribe Lisinopril or explore other treatment options is no easy task. On one hand, this commonly used ACE inhibitor has many benefits for heart health. On the other hand, there is potential for changes in metabolism to occur. As we continue to actively study and learn more about the effects of Lisinopril, let's prioritize staying up-to-date on discoveries to ensure we make informed decisions that prioritize our patients' overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions about Lisinopril and Diabetes
- Can diet and lifestyle modifications mitigate the potential impact of Lisinopril on blood glucose levels? - Absolutely. Adopting a balanced diet rich in whole foods and emphasizing fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, along with regular physical activity, can contribute to better metabolic health and may help counteract any potential effects of Lisinopril on blood glucose.
- Are there specific dietary recommendations for individuals taking Lisinopril to manage or prevent diabetes? - While there are no specific dietary restrictions, individuals on Lisinopril may benefit from monitoring their carbohydrate intake and choosing complex, fiber-rich carbohydrates. Maintaining a diet low in added sugars and saturated fats also supports cardiovascular and metabolic health.
- Are there alternative nutritional strategies for hypertensive individuals wary of Lisinopril's potential impact on blood glucose? - Certainly. Incorporating heart-healthy foods like oily fish, nuts, seeds, and potassium-rich fruits and vegetables can complement hypertensive management. Collaborating with a nutrition professional can help tailor dietary plans to individual needs, ensuring a well-rounded approach to blood pressure and metabolic health.

