Our health is our most valuable asset, and one of the most serious health problems today is diabetes. This is a chronic disease that can have a profound impact on the quality of life, from cardiovascular problems to kidney failure and even blindness.
Early detection and treatment of diabetes can reduce many dangerous complications. Therefore, understanding the testing methods and monitoring blood sugar levels is extremely important.
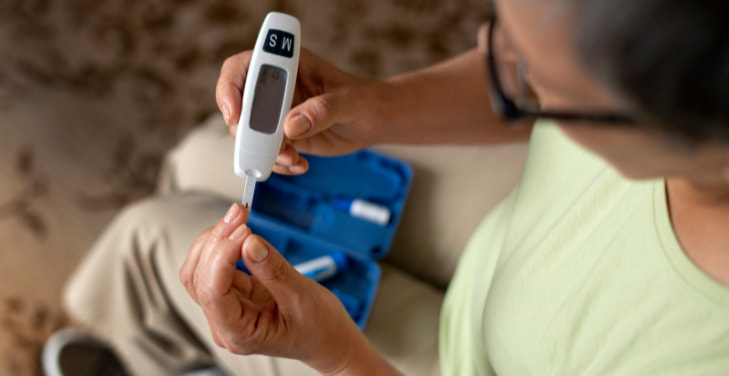
Learn how to test for diabetes with simple blood sugar checks.
Symptoms That May Indicate You Should Get Tested
When your body isn't functioning properly, it can sometimes be a warning sign that something is going on inside. Especially with diabetes, an increasingly common disease, early detection through symptoms can help prevent serious complications. Here are the symptoms you shouldn't ignore.
Frequent urination, constant thirst
One of the easily recognizable signs of diabetes is frequent urination and constant thirst. When blood sugar levels are uncontrolled, your body will try to eliminate sugar through urine, leading to dehydration and making you feel thirsty.
Fatigue and unexplained weight loss
You will feel tired and weak when your body can't convert sugar into energy efficiently. At the same time, changes in metabolism can also cause you to lose weight quickly without explaining the reason.
Blurry vision and persistent infections
Vision problems, such as blurred vision, are a worrying sign and a susceptibility to recurring infections. This occurs when persistently high blood sugar levels damage the small blood vessels in the body, especially in the eyes and skin.
If you notice these symptoms, talk to your doctor to check your blood sugar levels and devise a timely treatment plan.
Different types of diabetes
Diabetes is not a simple disease, but it comes in many different forms, each with its characteristics and requiring its treatment. Understanding the types of diabetes is the first step to helping you identify and manage the disease effectively.
Type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes, also known as insulin-dependent diabetes, is when the body's immune system attacks and destroys the beta cells in the pancreas, which produce insulin. This disease usually occurs in children and adolescents, requiring lifelong insulin injections to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Type 2 diabetes
This is the most common type of diabetes, occurring mainly in adults. Type 2 diabetes involves a condition where the body is resistant to insulin, meaning that although insulin is still produced, the cells cannot use it effectively. Although it can be controlled through diet, exercise, and medication, in many cases, patients need insulin when the condition becomes severe.
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a condition in which pregnant women develop high blood sugar levels, which can affect the health of both mother and fetus. However, the condition usually goes away after delivery. However, women who have had gestational diabetes are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future.
Understanding each type of diabetes will help you have more effective prevention and treatment strategies, leading to a healthier and more active life.
How to Test for Diabetes – Diagnosis Methods
Diagnosing diabetes is not always easy, as symptoms can be very subtle or not appear until the disease becomes severe. However, modern testing methods help detect diabetes early, allowing timely treatment to prevent complications.
Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) test
The FPG test measures blood sugar levels after fasting for at least 8 hours. If the result is above 126 mg/dL, the patient can be diagnosed with diabetes. This is a simple and popular method to detect diabetes.
HbA1c (A1C) test
A1C measures average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months through changes in hemoglobin in the blood. An A1C level above 6.5% indicates diabetes, while a level between 5.7% and 6.4% is a sign of prediabetes.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
This method involves drinking a glucose solution and measuring blood sugar levels after 2 hours. If blood sugar levels exceed 200 mg/dL after 2 hours, the person may have diabetes.
Random blood sugar test
This is a quick method to detect diabetes, measuring blood sugar levels at any time of the day. If blood sugar levels exceed 200 mg/dL and there are symptoms of diabetes, this is a sign of diagnosis.
Each testing method has advantages and disadvantages, but combining the results from multiple tests will help the doctor make an accurate and timely diagnosis.
Preparing for a Diabetes Test
Preparing for a diabetes test is an important step in the diagnostic process, helping to ensure accurate and reliable results. Depending on the type of test you need to perform, the preparation process may have special requirements. Here are some tips to help you best prepare for your diabetes tests.
Preparing for a fasting plasma glucose (FPG) test
You must fast for at least 8 hours before the test for the most accurate results. This means not eating or drinking anything except water during this time. Your fasting blood sugar level will best reflect your health at the beginning of the day.
Preparing for an HbA1c (A1C) test
The A1C test does not require fasting, but for accurate results, you should make sure that factors such as stress, illness, or medications you are taking do not affect your blood sugar level. Consult your doctor if you are taking any medications.
Preparing for the Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
For this test, you must fast overnight and be asked to drink a glucose solution after the initial test. You should be mentally prepared for this process, as it may cause you to feel a little uncomfortable for a short period.
Ensure you follow your doctor's instructions and don't skip any steps to ensure accurate and reliable test results.
Understanding the Results
When testing for diabetes, understanding your test results is an important step in determining your health status and appropriate treatment, each test provides different information about your blood sugar levels, and deciphering these numbers helps you make informed medical decisions.
Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) Test
This test shows your blood sugar level after an overnight fast. You have normal blood sugar if your result is below 100 mg/dL. If it is between 100 and 125 mg/dL, you may have prediabetes. A level above 126 mg/dL is a clear sign of diabetes.
HbA1c (A1C) Test
The A1C result reflects your average blood sugar level over the past 2-3 months. A level below 5.7% is normal. Between 5.7% and 6.4% is a sign of prediabetes. A level of 6.5% or higher usually indicates diabetes.
Oxygen Tolerance Test (OGTT)
A result above 200 mg/dL after 2 hours of drinking a glucose solution may indicate diabetes. A result between 140 and 199 mg/dL may indicate prediabetes.
The results of these tests will help your doctor determine your condition and advise you on appropriate treatment.
Monitoring and next steps
Once you have been diagnosed with diabetes, regular monitoring and taking the next steps are important for effective management of the disease. This not only helps control blood sugar levels but also prevents dangerous complications.
Regular blood sugar monitoring
One of the most important factors in diabetes management is daily blood sugar control. To ensure no large fluctuations, patients should use a blood sugar meter to monitor blood sugar levels at least several times a day, especially before and after meals.
Lifestyle and diet changes
Diet is a key factor in controlling diabetes. Patients must focus on eating foods with a low glycemic index, reducing carbohydrate intake, and maintaining a healthy, high-fiber diet. Combined with regular exercise, at least 30 minutes a day, will help increase the effectiveness of blood sugar control.
Medication and Insulin Treatment
If diet and lifestyle are insufficient to control blood sugar, your doctor may prescribe medication or order insulin treatment. Diabetes medication use needs to be monitored regularly to adjust the dosage to suit the patient's health condition.
Regular Health Checkups
Patients with diabetes need regular health checkups to monitor for possible complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, and eye problems. Keeping up with follow-up appointments with your doctor can help prevent serious health problems.
These monitoring and treatment steps need to be done continuously and seriously to ensure that the patient can live a healthy life and minimize the risks caused by diabetes.
Conclusion
Early detection and diagnosis of diabetes are key to effectively managing the disease. Diabetes tests, from FPG to A1C, provide a comprehensive view of a patient's blood sugar levels and health status.
It is important to recognize the disease and maintain a continuous care regimen, including monitoring blood sugar levels, adjusting diet, and using medications when necessary.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- How do I know if I am at risk for diabetes? - Factors such as family history, sedentary lifestyle, overweight, and age are major risk factors. Regular blood sugar testing will help determine the exact risk.
- Can I test for diabetes at home? - Yes, through home blood sugar measuring devices. However, testing at a medical facility still provides more accurate results and helps doctors make the right diagnosis and treatment.
- Can diabetes be cured? - Currently, diabetes cannot be completely cured. However, the disease can be well controlled through diet, exercise, medication, and regular monitoring.
- What complications can diabetes cause? - If not well controlled, diabetes can lead to serious complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, blindness, or nerve damage, greatly affecting the quality of life.
- Why do I need an A1C test? - The A1C shows your average blood sugar level over the past 2-3 months. This test helps your doctor evaluate the effectiveness of your treatment and adjust your diet and exercise regimen.

