Health and fitness are the foundation of an active and resilient life. Creatine – a supplement trusted by millions – is the key to unlocking the hidden power within your body.
Increasing energy, breaking training limits, and improving sports performance are what creatine brings powerfully and clearly.
The journey to discover the correct and scientific dosage will help you make the most of this power, turning each workout into a breakthrough step.
Creatine dosage depends on goals, with standard loading and maintenance recommendations.
Understanding Creatine and Its Function
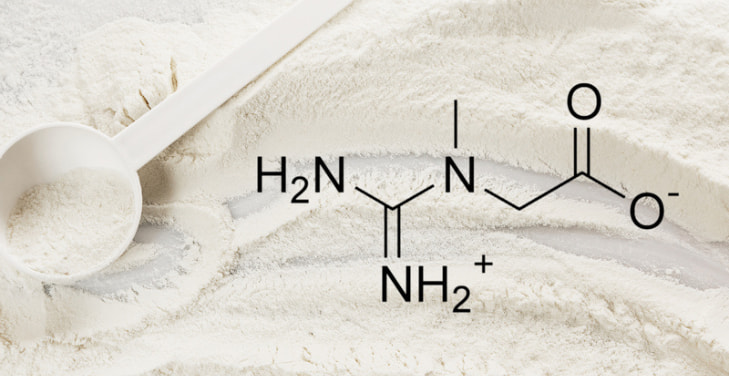
Creatine is a natural compound synthesized from amino acids. It is present in large quantities in the muscles and brain. It is a quick energy source, providing instant “fuel” for short-term, high-intensity activities.
Role in the body
Creatine is stored in the muscles as phosphocreatine, participating in the regeneration of ATP—an essential energy molecule for all movements. When exercising, creatine helps maintain strong muscle contractions, reducing performance decline in consecutive sets.
Performance support mechanism
Increasing the creatine in the muscles helps the body create ATP faster. This supports increased strength, improved recovery speed, and optimized load-bearing capacity in heavy exercises.
Long-term effects
Reasonable creatine supplementation improves athletic performance and supports neurological health and cognitive function.
→Explore the science behind creatine in our What Is Creatine guide.
Recommended Daily Creatine Dosage
The daily creatine dosage plays a decisive role in the supplement's effectiveness. It helps the body achieve a state of saturation and maintains optimal energy levels for the muscles. The standardized number is based on many scientific studies and is suitable for most exercisers and athletes.
Standard maintenance dose
The commonly recommended dose is 3–5 grams of creatine per day. This is enough to maintain high levels of creatine stores in the muscles after the loading phase, or to gradually increase without the need for an initial loading phase.
Scientific basis
Studies show that 3–5 grams/day doses help optimize phosphocreatine synthesis, thereby supporting rapid and continuous ATP regeneration during exercise.
Adjust to individual needs
Those with large muscle mass or high-intensity training may choose a level closer to 5 grams/day to ensure maximum effectiveness. Consistency in supplementation is key to maintaining long-term results.
The Loading Phase Explained
The creatine loading phase rapidly increases muscle creatine stores to saturation. This shortens the waiting period, allowing users to experience increased strength and performance sooner.
Standard loading dose
A common loading dose is 20 grams of creatine per day, divided into four doses, continuously maintained for 5–7 days. The split dose allows for better absorption and reduces the stress on the digestive system.
The goal of the loading phase
The rapid increase in phosphocreatine stores allows the body to produce ATP almost instantly during high-intensity exercise. This improves strength, short-term endurance, and recovery speed.
Pros and cons
The obvious advantage is that it is fast-acting, especially useful when preparing for a heavy training phase or competition. Potential downsides include the need to closely monitor water intake and accompanying diet to optimize effects.
Maintenance Phase Guidelines
The creatine maintenance phase is the next step after muscle saturation. Its purpose is to maintain stable stores and ensure long-term training performance. This is the optimal time to balance effectiveness and convenience in supplementation.
Recommended maintenance dose
A common level is 3–5 grams of creatine per day, taken regularly to maintain high muscle phosphocreatine levels. This amount is enough to compensate for the natural loss of creatine due to physical activity.
Duration of use
The maintenance phase can last several weeks to months, depending on your goals and training schedule. Regular maintenance helps keep your muscles ready to meet immediate energy needs.
Benefits of maintenance
Steady supplementation helps preserve strength, increase recovery between workouts, and support neuromuscular health. This is the foundation for achieving sustainable results in bodybuilding and sports.
Timing: When to Take Creatine
The timing of creatine supplementation directly affects the rate of absorption and the muscles' ability to utilize energy. The right combination of intake time and training schedule creates a significant advantage for performance and recovery.
Pre-workout
Taking creatine before training helps provide a ready source of phosphocreatine, which supports explosive movements and enhances strength during the workout.
Post-workout
After training with carbohydrates or protein, supplementing creatine increases insulin transport into the muscles, supporting ATP regeneration and muscle tissue repair.
Consistency
The key is to maintain daily supplementation at a fixed time frame. This stability helps keep creatine levels in the muscles at optimal levels, ready to meet the demands of exercise at any time.
Factors That Affect Dosage
The optimal creatine dose depends on several physiological and lifestyle factors. Identifying these factors can help individualize supplementation to maximize benefits and maintain long-term effectiveness.
Body Mass and Muscle Mass
Heavier and leaner individuals may require higher amounts of creatine to achieve similar saturation levels than smaller individuals.
Diet
People who regularly consume red meat or fish get some of their creatine naturally from food, so their supplemental needs may be lower than those of vegetarians or those who consume little animal protein.
Training Intensity and Goals
Heavy, high-frequency training sessions or those aiming for maximal strength may require maintenance doses closer to 5 grams/day. Conversely, moderate exercise may be effective with doses lower than recommended.
Safety and Overuse Risks
Creatine is considered safe when used in the right dose, but taking more than your physiological needs can put unnecessary stress on your body. Understanding the limits helps maintain benefits while ensuring long-term health.
High-dose risks
Continuous use of large amounts of creatine can increase the filtration load on the kidneys and cause digestive discomfort. These symptoms often appear when the supplement is far above the recommended level.
Water retention and changes in body mass
Creatine increases intracellular water reserves, leading to a feeling of fullness or rapid weight gain. This is a normal physiological response, but should be monitored in people with strict weight requirements.
Safety principles
Always supplement with enough water, divide the dose reasonably throughout the day, and maintain a balanced diet. This combination helps optimize efficiency while keeping the body in a stable state.
Expert Tips for Optimal Results
Effective creatine supplementation requires adherence to dosage and a combination of a proper nutrition strategy and training routine. Applying expert tips helps maximize absorption and maintain sustainable results.
Combine with carbohydrates or protein
Using creatine with a quality carb or protein source helps increase insulin, thereby promoting creatine transport into muscle cells faster and more effectively.
Stay hydrated
Drinking enough water daily ensures a favorable intracellular environment for creatine storage and supports energy-related metabolic processes.
Track progress
Record strength, performance, and muscle mass indexes through each stage to adjust the supplementation plan promptly. This initiative helps the body adapt well and maintain long-term effectiveness.
Conclusion
Creatine is a powerful performance enhancer when used consistently and in the right dosage. It optimizes energy production, improves strength, accelerates recovery, and supports neuromuscular health.
Adhering to loading and maintenance phases and incorporating the right supplementation strategy helps achieve sustainable results. Actively monitoring and adjusting dosages creates long-term benefits for health and athletic performance.
→Discover potential impacts in our Creatine Side Effects in Men guide.
Frequently Asked Questions About Creatine
-
How much creatine should I take daily?
The standard dose is 3–5 grams per day to maintain muscle creatine stores, helping to support continuous energy and strength during training. -
Do I need to load creatine?
A loading phase of 20 grams/day for 5–7 days helps to quickly saturate muscle creatine, shortening the time to achieve optimal results. -
When is the best time to take creatine?
The optimal time is before or after training, combined with carbohydrates or protein to increase absorption and effective recovery. -
Does creatine have side effects?
Supplementing at the right dose is safe, but overdose can cause digestive discomfort and increase kidney load, so drink enough water and monitor your health. -
Can I take creatine if I am a vegetarian?
Vegetarians should supplement creatine because a diet lacking in animal products does not provide enough, helping to maintain energy and effective training strength.

