Creatine has long been a fascinating mystery in the world of sports nutrition. Inside each muscle fiber, this tiny compound acts as a "power key," unlocking the potential for explosive power.
The body produces creatine naturally and absorbs it from food and supplements. When stored sufficiently, creatine triggers biochemical reactions that help maintain performance, speed recovery, and support muscle growth.
Understanding the mechanism of creatine is the first step to maximizing your athletic potential.
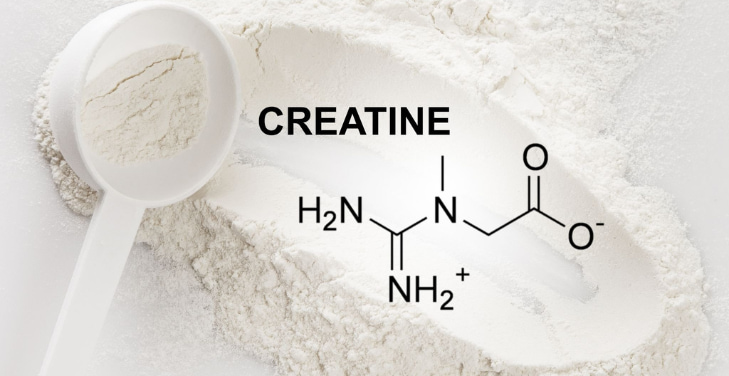
How does creatine work?
What Is Creatine?
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound found primarily in skeletal muscle. It is essential for providing energy for high-intensity physical activity. The body synthesizes creatine from amino acids in the liver, kidneys, and pancreas and then transports it to the muscles for storage as creatine phosphate.
Dietary and Supplemental Sources
Creatine is abundant in red meat, fish, and some protein-rich foods. However, dietary intake is often insufficient for intensive training, so supplementing creatine in powder or tablet form has become popular.
Basic Biological Role
Creatine participates directly in the ATP-PCr system, helping rapidly regenerate adenosine triphosphate - the main energy source for explosive activities such as weightlifting and sprinting. The presence of adequate creatine in the muscles helps maintain strength, increase performance, and support recovery.
→Learn more in our full article What Is Creatine?
Creatine's Role in Energy Production
Creatine is a strategic link in the body's rapid energy supply chain. During high-intensity exercise, ATP demand spikes, and creatine phosphate becomes an instant "charger." It releases phosphate to regenerate ATP, ensuring that muscles continue to work vigorously.
ATP-PCr System
The ATP-phosphocreatine system operates in the first few seconds of each explosive movement. Creatine phosphate in the muscles donates energy-rich phosphate groups to ADP, forming new ATP and fueling muscle contraction.
Implications for performance
Abundant creatine stores extend the ability to sustain high power output, supporting fast, powerful movements such as jumping, weightlifting, or sprinting. Efficient ATP regeneration also shortens recovery time between sets.
Comprehensive impact
In addition to muscles, creatine also provides energy to nerve cells, optimizing reflexes and the ability to concentrate during intensive exercise.
Effect on Muscle Performance
Creatine provides a distinct biological advantage for muscle strength and endurance. With ATP replenished quickly, muscles can maintain maximum performance over multiple sets, reducing fatigue and increasing overall performance.
Increased Strength and Power
Creatine supplementation increases creatine phosphate stores, which supports greater muscle contraction force and faster movement speed. This is especially useful for high-power activities such as weightlifting, sprinting, or competitive sports.
Improved Training Capacity
The ability to sustain high intensity over multiple sets allows muscles to withstand load for longer. This accumulation stimulates optimal muscle adaptation and growth.
Supports Recovery
Creatine promotes energy resynthesis between sets, reduces metabolic stress, and supports muscle fiber repair, preparing muscles for the next training cycle.
Cellular and Muscle-Level Impact
Creatine works deeply at the cellular level, creating an intracellular environment conducive to muscle growth and function. When adequately stored, creatine promotes key biochemical processes that help the body maintain muscle performance and growth.
Increases intracellular water retention
Creatine draws water into muscle cells, increasing cell volume and muscle fiber expansion. This expansion triggers anabolic signals, facilitating protein synthesis and building lean muscle mass.
Supports protein synthesis
The high-energy, water-rich intracellular environment helps ribosomes function more efficiently, thereby increasing the rate of muscle protein production, strengthening muscle structure and strength.
Reduces muscle breakdown
Creatine provides a quick energy source for cells, limiting the body's need to use muscle protein for energy, preserving muscle mass, and supporting recovery after exercise.
Benefits for Brain Function
Creatine supports muscles and plays an essential role in brain function. The brain consumes much energy to maintain nerve conduction, process information, and regulate reflexes. Creatine provides an additional source of energy, helping to optimize cognitive performance.
Enhance brain energy metabolism
Creatine phosphate participates in ATP regeneration in nerve cells, ensuring a continuous energy source for synapses to function and maintain the speed of nerve signal processing.
Reduce mental fatigue
Creatine supplementation helps maintain stable energy levels for the brain, limiting the decline in performance when doing high-intensity mental work or under prolonged stress conditions.
Support cognitive function
Creatine improves short-term memory, concentration, and reflex speed. This effect is especially evident in situations that require fast processing, such as sports competitions or high-precision work.
Factors That Influence How Creatine Works
The effectiveness of creatine depends on many physiological and lifestyle factors, from dosage to nutritional status. Understanding these factors helps optimize creatine's impact on performance and overall health.
Dosage and loading phase
Starting with a 20g/day loading phase in divided doses for 5–7 days and maintaining 3–5g/day helps rapidly increase muscle creatine stores and stabilize long-term effectiveness.
Body composition and activity type
Individuals with large muscle mass or who engage in strength and explosive training often need more creatine to meet their high energy demands.
Diet and hydration status
Supplementing creatine with carbohydrates or protein supports optimal absorption. Maintaining adequate hydration throughout the day helps create a favorable environment for intracellular creatine storage.
Safety, Usage, and Best Practices
Creatine is one of the most well-researched and well-regarded supplements when used properly. A proper strategy can help maximize effectiveness and maintain long-term health and performance benefits.
Proven Safety Profile
Many long-term studies confirm that creatine is suitable for healthy people in the recommended dosage. Monitoring one's body's response during use helps personalize the dosage.
Optimal Timing and Usage
Supplementing creatine immediately after exercise with carbohydrates or protein helps boost muscle absorption and storage. Splitting the dose into multiple doses throughout the day helps reduce digestive pressure.
Consult a professional when needed
People with underlying medical conditions or taking medications should consult a physician or sports nutritionist to develop an appropriate supplementation plan.
Conclusion
Creatine is a strategic compound that helps to rapidly regenerate energy, enhance strength, and support muscle recovery. Its effects extend to the brain, improving cognitive performance and reducing mental fatigue.
Using creatine in the right dose, at the right time, and with a reasonable diet will bring optimal results for both physical performance and long-term health.
→Discover more in our full article Dangers of Creatine.
Frequently Asked Questions About Creatine
-
How does creatine work?
Creatine is stored as creatine phosphate in the muscle. It rapidly regenerates ATP, providing instant energy for explosive activities such as weightlifting or sprinting and aiding muscle recovery between sets. -
Is creatine safe for long-term use?
Long-term studies have shown that creatine is safe for healthy people when recommended doses are followed, combined with proper nutrition and adequate hydration to maintain performance and overall health. -
Does creatine help build muscle faster?
Creatine creates a favorable intracellular environment, increases water retention, and supports protein synthesis, stimulating muscle growth, increasing strength, and endurance during high-intensity training. -
When should you take creatine?
Taking creatine immediately after a workout with carbohydrates or protein increases its uptake and storage in the muscle, optimizing recovery and improving performance for subsequent workouts. -
Who should consider creatine supplementation?
Strength trainers, explosive athletes, or those looking to improve muscle recovery can all benefit from creatine, especially when combined with a high-protein diet and a structured training plan.

