The ear canal is an indispensable part of the auditory system, playing an important role in receiving and transmitting sound. However, few people realize that the ear canal's health can determine the hearing quality.
When the ear canal has problems such as blockage, infection, or damage, it can seriously affect hearing ability. Therefore, understanding the structure, function, and problems related to the ear canal is essential to protect hearing health.
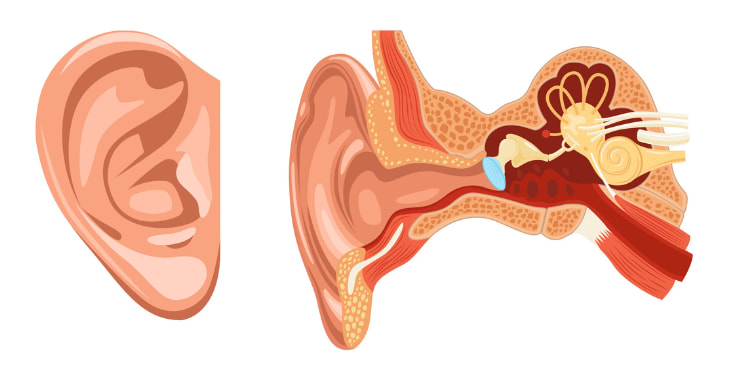
The ear canal helps direct sound waves to the eardrum.
Ear Canal
The ear canal, also known as the external auditory canal, is an essential part of the human ear structure, playing an important role in receiving and transmitting sound. With a length of about 2.5 cm in adults, the ear canal is a tubular tube extending from the auricle to the eardrum, which contacts the middle ear.
Structure and Characteristics
The ear canal is divided into three main parts: the outermost part is made of cartilage, the middle part is a combination of bone and cartilage, and the innermost part is adjacent to the eardrum, usually made of hard bone. The surface of the ear canal is covered by a thin layer of skin containing ceruminous glands that produce ear wax, helping to protect the ear canal from bacteria, dirt, and harmful agents from the environment.
Function and Protection
The main function of the ear canal is to transmit sound waves from the external environment to the eardrum. In addition, the ear canal also protects the sensitive structures inside the ear, thanks to ear wax and the activity of the cilia inside. The perfect combination of these factors helps maintain hearing health and prevent ear-related diseases.
Anatomy of the Ear Canal
The ear canal, an important part of the auditory system, is not only a path for sound transmission but also a complex organ with a special structure. From the auricle to the eardrum, the ear canal is about 2.5 cm long in adults and has a slightly curved tube shape.
Structure and Parts of the Ear Canal
The ear canal is divided into three main parts: the outermost part is made of cartilage, the middle part is a combination of bone and cartilage, and the innermost part adjacent to the eardrum is made mainly of bone. The surface of the ear canal is covered with a thin layer of skin, which contains ceruminous glands responsible for producing ear wax, a natural protective substance.
Important Functions
In addition to transmitting sound waves to the eardrum, the ear canal also protects the internal auditory structures. The ear wax layer and cilia in the canal help prevent dirt, bacteria, and harmful agents from entering, ensuring a clean environment and protecting hearing health.
Functions of the Ear Canal
The ear canal is not only a path for sound transmission but also performs many important functions for the health of the ear and the auditory system. Designed with a special structure, the ear canal cancan protect and support the effective hearing process.
Sound Wave Conversion and Sound Transmission
The main function of the ear canal is to transmit sound waves from the external environment to the eardrum, where these waves will be converted into electrical impulses and transmitted to the brain. The curved shape and size of the ear canal help optimize the reception of sound from all directions, especially medium frequencies, helping people hear clearly and in detail.
Protecting and Cleaning the Ear Canal
In addition to its hearing function, the ear canal also protects the sensitive parts inside the ear. Ear wax secreted from ceruminous glands can prevent dirt, bacteria, and water from entering, while the cilia in the canal help keep it clean and protected from harmful agents.
Common Ear Canal Problems and Disorders
Although playing an important role in hearing and protecting the ear structures, the ear canal is also susceptible to several problems and disorders that can affect the ear's health. These conditions can cause discomfort and even hearing loss if not treated promptly.
Ear Wax Blockage and Buildup
One of the most common ear canal problems is the buildup of wax, which can block the ear canal and reduce the ability to conduct sound. Wax can build up due to improper hygiene or overproduction of ceruminous glands. Symptoms include a feeling of stuffiness, pain, or even hearing loss. Treatment is primarily focused on the safe removal of wax.
Ear Infections and Infections
Infections, such as otitis externa, are usually caused by bacteria or fungi and can cause itching, swelling, redness, and pain. Water or dirt entering the ear canal, especially when exposed to a moist environment, is the main cause of infection. Treatment includes antibiotics or antifungal medications, depending on the cause.
Trauma and Mechanical Injury
Trauma from improper use of objects, such as earrings or foreign objects, can cause damage to the ear canal and eardrum, leading to inflammation, infection, or even perforation of the eardrum. This damage needs to be treated immediately to avoid long-term effects on hearing.
Tips for Maintaining Ear Health
Proper care and hygiene are extremely important to ensure that your ear canal stays healthy and your hearing function is not impaired. Some simple but effective habits can help protect your ear canal from harmful agents.
Proper Ear Hygiene
Avoid using cotton swabs or sharp objects to clean your ear canal, as this can push ear wax deeper inside and cause blockage. Instead, simply wipe the outside of your ear with a damp cloth. You can use ear drops or see a doctor to safely remove ear wax for a deep clean.
Protect Your Ears from Infection
To prevent infections, especially otitis externa, keep your ears dry and avoid prolonged exposure to water, especially during swimming activities. When exposed to humid environments, use headphones or earplugs to protect your ear canal from bacteria and fungi.
Regular Ear Checkups
See an ENT doctor regularly for early detection of problems related to the ear canal. Regular ear checkups help detect signs of inflammation, blockage, or infection early, providing appropriate treatment options.
Ear Canals Related to Hearing Loss
The ear canal is the part that conducts sound from the outside to the eardrum and plays an important role in maintaining hearing ability. Problems in the ear canal can directly affect the hearing process, leading to hearing loss.
Blockage and Hearing Effects
One of the main causes of temporary hearing loss is blockage of the ear canal due to wax buildup. When wax builds up, it can block sound transmission to the eardrum, causing a feeling of stuffiness, reduced hearing ability, and sometimes pain. Safe removal of ear wax can restore normal hearing ability.
Infections and Damage to the Ear Canal
Infections of the ear canal, such as otitis externa, can cause inflammation, affecting the ability to transmit sound to the middle ear. Not treating this condition promptly can lead to permanent damage, resulting in hearing loss. Furthermore, mechanical trauma to the ear canal, such as using sharp objects for cleaning, can cause lacerations or serious infections, affecting hearing.
Conclusion
The ear canal plays an essential role in the hearing system, from transmitting sound to protecting the structures inside the ear. The perfect combination of structure and function of the ear canal helps maintain hearing health and prevent potential problems.
Understanding the problems and disorders in the ear canal and maintaining proper hygiene and care are key to long-term ear health. Proper ear canal care will ensure good hearing and prevent unwanted risks.
Related Articles
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What role does ear wax play in the ear canal? – Ear wax helps protect the ear canal from dirt, bacteria, and water. It also keeps the ear canal moist, preventing infection and maintaining a clean environment for the eardrum.
- Why can the ear canal become blocked? – Ear canal blockage is mainly caused by ear wax buildup or dirt getting in, which interferes with sound transmission. Using the wrong items or not cleaning properly can make this condition worse.
- How to clean the ear canal safely? – Clean the ear canal safely using warm water or a specialized solution to gently wash. Avoid using cotton swabs or sharp objects to clean, as they can damage the ear canal or eardrum.
- What problems can an ear canal infection cause? – An ear canal infection can lead to inflammation, pain, swelling, and temporary hearing loss. If not treated promptly, the infection can cause permanent damage to the inner ear structures.
- How can the ear canal affect hearing? – Problems such as wax blockage, infection, or damage to the ear canal can reduce the ability of sound to reach the eardrum, causing temporary or permanent hearing loss if not treated properly.

