Diabetes is a rapidly growing global health problem, affecting millions of people each year. Although it can be controlled with medication and lifestyle changes, managing blood sugar levels remains a major challenge.
Uncontrolled blood sugar levels can lead to serious complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, and nerve problems. Therefore, monitoring and regulating blood sugar is key to maintaining health for people with diabetes.
With the right care, patients can live healthy lives and effectively control their diabetes.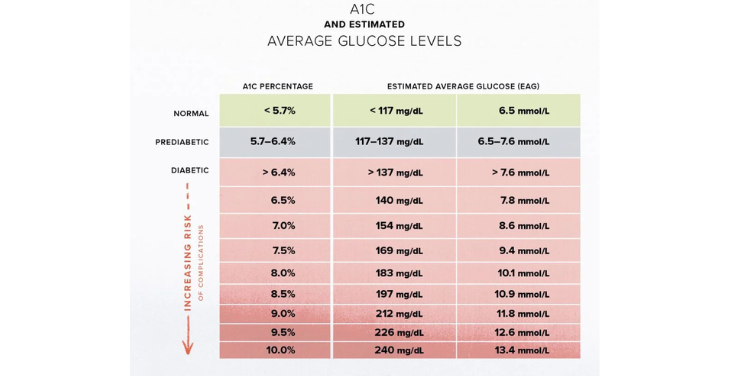
Blood sugar levels for diabetes charts simplify glucose management.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar, or glucose concentration in the blood, is an important factor in maintaining health and hormonal balance. When the body cannot regulate blood sugar effectively, serious health problems, including diabetes, can arise. A thorough understanding of blood sugar levels can not only help diabetics manage their condition but also provide valuable insights for those looking to prevent it.
Types of Blood Sugar Levels
Fasting Blood Sugar Level: Measures blood sugar levels after not eating or drinking for 8–12 hours. This level helps assess the body's ability to control glucose at baseline.
Postprandial Blood Sugar Level: Measured two hours after a meal, it provides a clear view of the body's response to food and its ability to control sugar.
The Importance of A1C
A1C is a measure of the average blood sugar level over three months. Although it does not directly measure individual spikes and dips in blood sugar, A1C is a reliable tool for assessing long-term diabetes control and predicting the risk of serious complications.
A clear understanding of these blood sugar levels not only provides the foundation for health care but is also key to preventing potential complications of diabetes.
Blood Sugar Chart for Diabetes
A blood sugar levels for diabetes chart provides a clear reference for understanding normal, prediabetic, and diabetic blood sugar ranges, including fasting, postprandial (after meals), and A1C levels. It helps individuals with diabetes monitor their glucose levels and adjust their treatment and lifestyle.
Fasting and Postprandial Blood Sugar Levels
Fasting Blood Sugar: This is the blood sugar level after the body has not eaten for at least 8 hours. The ideal blood sugar level for healthy people ranges from 70 to 99 mg/dL, while for diabetics, this number can be up to 130 mg/dL or higher.
Postprandial Blood Sugar: Measured 2 hours after a meal, the ideal blood sugar level below 140 mg/dL is a sign of good control. However, if it exceeds this threshold, the patient may have glucose control problems.
The Role of A1C
The A1C, which shows the average blood sugar level over three months, is an important component of the blood sugar chart. The higher the A1C, the greater the risk of developing diabetes complications, which further emphasizes the importance of maintaining a stable blood sugar chart.
Regular monitoring and understanding of blood sugar charts is an important strategy in preventing diabetes complications helping patients maintain a healthy and fulfilling life.
How to Check and Monitor Blood Sugar
Checking and monitoring blood sugar is an essential part of diabetes management. It helps patients maintain stable glucose levels, avoid dangerous complications, and optimize treatment strategies. However, this requires patience and a thorough understanding of measurement tools and techniques.
Methods of Checking Blood Sugar
Blood Glucose Meter: This method uses a test strip to take a blood sample from the fingertip and then insert it into the meter to determine the glucose level. This is the main tool for home blood sugar monitoring, providing fast and accurate results.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): CGM provides real-time information about blood sugar levels, allowing users to track glucose fluctuations throughout the day without pricking their fingers frequently. This is modern technology helping to improve long-term diabetes management.
Benefits of Regular Monitoring
Monitoring blood sugar levels helps detect dangerous fluctuations early and allows patients to adjust their diet, exercise, and medications accordingly. Recording and sharing the results with your doctor regularly will help you make more accurate treatment decisions.
With the support of modern testing methods, blood sugar management is no longer a challenge but part of a comprehensive health care strategy.
Blood Sugar Targets for Different Types of Diabetes
Each type of diabetes has its blood sugar target requirements, and understanding these targets is crucial to managing and preventing complications. For each group of patients, from type 1 to type 2 to gestational diabetes, these targets must be adjusted to suit the health status and individual treatment strategy.
Targets for Type 1 Diabetes
Patients with type 1 diabetes need to maintain blood sugar levels between 80–130 mg/dL when fasting and below 180 mg/dL after meals. However, insulin adjustments and regular monitoring are necessary to avoid episodes of excessive hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia.
Targets for Type 2 Diabetes
For type 2 diabetes, blood sugar targets range similarly but require a close combination of diet, exercise, and medication. The ideal blood sugar level is below 130 mg/dL when fasting and below 180 mg/dL after meals.
Targets for Gestational Diabetes
Although gestational diabetes can resolve after delivery, blood sugar control during pregnancy is extremely important to avoid risks for both mother and fetus. Target blood sugar levels for pregnant women are usually below 95 mg/dL when fasting and below 120 mg/dL after meals.
Setting blood sugar targets appropriate for each type of diabetes helps patients maintain their health and is a key factor in preventing long-term complications.
Tips for Controlling Blood Sugar
Controlling blood sugar is one of the most important factors for people with diabetes, contributing not only to maintaining health but also preventing serious complications. Here are some tips to help regulate glucose levels effectively and sustainably.
Healthy Diet
Diet plays a key role in controlling blood sugar. Choosing foods with a low glycemic index, such as whole grains, fresh fruits and vegetables, and foods rich in fiber, helps maintain stable blood sugar levels. Limiting the consumption of simple sugars and processed foods is essential.
Regular Exercise
Physical activity helps burn calories and improve insulin sensitivity, thereby helping the body use glucose more effectively. Exercises such as walking, swimming, or yoga can all help control blood sugar.
Managing Stress and Getting Enough Sleep
Prolonged stress can increase cortisol levels, leading to increased blood sugar. Practice daily relaxation and ensure you get 7–8 hours of sleep each night to support your endocrine system and maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring
Daily blood sugar testing and charting help patients understand fluctuations in glucose levels and make timely adjustments to diet, medication, and lifestyle. In particular, recording the results helps doctors make accurate treatment decisions.
Regularly applying these tips will help you control your blood sugar while improving your quality of life and preventing long-term complications.
Risks of High and Low Blood Sugar
Both high and low blood sugar levels pose serious health risks, especially for people with diabetes. Poor glucose control can lead to acute and chronic complications that affect quality of life and longevity.
Risks of Hyperglycemia
When blood sugar levels exceed the safe level (above 180 mg/dL after meals), the body cannot use glucose effectively, causing fatigue, thirst, and frequent urination. If left unchecked, this condition can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or hyperosmolar coma, which are life-threatening conditions. Increased monitoring and adjustment of insulin doses are necessary to prevent these complications.
Risk of Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia)
A blood sugar level below 70 mg/dL is considered hypoglycemia, with symptoms such as dizziness, shakiness, confusion, and even fainting. Hypoglycemia occurs when the body receives too much insulin or does not get enough energy from food. Without timely intervention, hypoglycemia can lead to coma or brain damage.
Careful and regular control of blood sugar levels is important in minimizing the risk of both conditions, thereby protecting health and preventing dangerous complications.
When to See a Doctor
Monitoring and controlling your blood sugar is essential to managing your diabetes. However, there are times when seeing a doctor is especially important to ensure that your health does not develop serious complications. Here are some signs that you need to see a doctor right away.
Severe Blood Sugar Fluctuations
If you notice that your blood sugar levels are fluctuating from too high to too low, even when you follow your diet and medication regimen, it's time to see your doctor. These changes may signal that your treatment regimen needs to be adjusted.
Unusual and Serious Symptoms
If you experience symptoms such as fatigue, constant thirst, frequent urination, or feeling dizzy and confused, these could be signs of complications such as osmolar coma or ketoacidosis – conditions that can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
High A1C Test Result
If your A1C test result is above your target range, your blood sugar levels over the past three months have not been well controlled. At this point, you should see your doctor to discuss adjusting your treatment plan and preventing long-term complications.
Seeing your doctor on time can help identify the root cause of your symptoms but also help adjust your treatment, reduce your risks, and protect your long-term health.
Conclusion
Controlling blood sugar levels is key to maintaining health and preventing complications for people with diabetes. Understanding blood sugar levels and regular monitoring helps patients adjust their diet, exercise, and medication effectively.
In addition, working closely with your doctor and attending regular checkups are essential to maintaining a comprehensive healthcare strategy. This protects your current health and helps reduce the risk of serious problems in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the ideal blood sugar level for people with diabetes? - The ideal blood sugar level for people with diabetes is below 130 mg/dL when fasting and below 180 mg/dL after meals. However, the specific goal may vary depending on the patient.
- Why is blood sugar control important? - Controlling blood sugar is important in preventing diabetes complications such as nerve damage, kidney failure, and heart problems. This helps maintain a better quality of life.
- How do you know when your blood sugar is too high or too low? - When blood sugar is too high, you may feel thirsty and tired. Dizziness, hand tremors, and confusion may appear when it is too low. Timely response is very important.
- Is it necessary to see a doctor regularly? - Regular visits to the doctor are important to adjust your treatment plan. If there are any changes in symptoms or blood sugar levels, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
- How to reduce the risk of diabetes complications? - To reduce the risk of complications, patients should maintain a healthy diet, exercise regularly, control stress, monitor blood sugar regularly, and fully comply with treatment.

